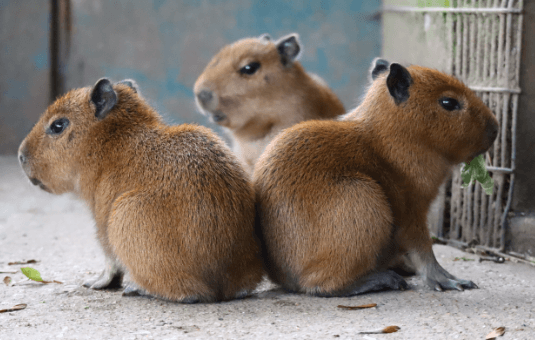
The early development of baby capybaras, or pups, presents intriguing insights into their adaptive behaviors and ecological roles. Born with acute sensory capabilities, these young animals quickly acclimate to their semi-aquatic environments, highlighting their evolutionary advantages. Their playful interactions not only strengthen familial bonds but also serve as a foundation for critical survival skills. However, the significance of their herbivorous diet and its impact on the ecosystem raises important questions about their role as both grazers and prey. What implications might these dynamics have for their habitat and the broader ecosystem?
Capybara Baby Characteristics
Capybara babies, known as pups, exhibit distinctive characteristics that facilitate their survival in the wild, including a well-developed sense of hearing and vision at birth, as well as a semi-aquatic adaptation that allows them to swim shortly after delivery.
Their early social bonding with family groups is crucial, while their dietary needs are met through a herbivorous diet, ensuring robust growth and health.
See also: Anime:Wekwakpraui= Wallpaper
Playful Behavior of Young Capybaras
Frequently observed in their natural habitats, young capybaras engage in playful behaviors that are essential for developing social bonds and honing survival skills.
Their playful antics often involve chasing, wrestling, and vocalizing, facilitating critical social interactions.
Through these activities, young capybaras not only strengthen their relationships within the group but also practice essential behaviors that enhance their adaptability and resilience in the wild.
Importance in Their Ecosystem
In the intricate web of their ecosystem, capybaras play a pivotal role as both grazers and prey, significantly influencing the dynamics of their habitat.
Their grazing habits contribute to ecosystem balance by controlling vegetation growth, while their presence supports biodiversity by serving as a food source for various predators.
Thus, capybaras are essential for maintaining ecological harmony and fostering a diverse array of life forms.
Conclusion
In summary, the early development and social interactions of capybara pups are akin to the foundational notes of a symphony, where each interaction contributes to the harmonious balance of their ecosystem.
As these young grazers learn vital survival skills through play and bonding, they not only enhance their own growth but also serve as a crucial food source for various predators.
Thus, the presence of capybara pups underscores the interconnectedness of species within their habitat, illustrating the delicate dance of nature’s design.