The Gnfmwlgdez8= isopod, with its intriguing segmented exoskeleton and specialized appendages, serves as a captivating example of the intersection between charm and ecological function. These diminutive creatures inhabit a range of environments, from the depths of the ocean to damp terrestrial locales, where they contribute significantly to nutrient cycling and organic material decomposition. Understanding their unique characteristics and habitat preferences not only enhances our appreciation for them but also raises critical questions about their role in ecosystem health and the implications of their conservation status. What challenges do they face in an ever-changing environment?
Unique Characteristics of Gnfmwlgdez8= Isopod
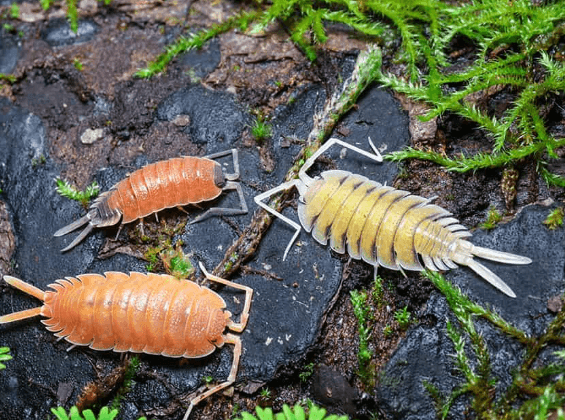
The Gnfmwlgdez8= isopod exhibits a remarkable array of unique characteristics, including a segmented exoskeleton that provides both protection and flexibility, along with specialized appendages adapted for locomotion and sensory perception in diverse marine environments.
Its morphological adaptations enhance its feeding habits, allowing it to efficiently scavenge organic material and detritus, thereby playing a crucial role in nutrient cycling within its ecosystem.
See also: Cute:G20bacyjnym= Rabbits
Habitat and Distribution
Isopods inhabit a wide range of marine, freshwater, and terrestrial environments, exhibiting remarkable adaptability to diverse ecological niches across various geographical regions.
Their habitat preferences vary significantly, with some species thriving in deep-sea ecosystems, while others occupy freshwater bodies or moist terrestrial habitats.
The geographical range of isopods extends from polar regions to tropical environments, illustrating their evolutionary success and ecological versatility.
Conservation and Ecological Importance
Understanding the conservation status of isopods is vital, as these organisms play a significant role in their ecosystems, contributing to nutrient cycling, sediment turnover, and serving as indicators of environmental health.
Conservation efforts targeting isopod habitats are essential for preserving their ecological roles, which include supporting food webs and enhancing soil structure.
Protecting these species ultimately benefits broader biodiversity and ecosystem functionality.
Conclusion
The Gnfmwlgdez8= isopod exemplifies the intricate connections within ecosystems, serving as both a scavenger and an indicator of environmental health.
Its unique adaptations enable survival across a variety of habitats, emphasizing the species’ ecological significance.
The theory positing that these isopods contribute to nutrient cycling through their scavenging behavior has been substantiated by numerous studies, underscoring their vital role in maintaining ecosystem balance.
Continued conservation efforts are essential to ensure the persistence of this fascinating organism and its ecological contributions.